CPT Write-up
This is the collegeboard requirements write-up for the CPT project.
Program Purpose and Function
Video
Link if the video doesn't work:https://clipchamp.com/watch/yoIxsQDvu2O
Purpose: The purpose of this web app is to allow users to reflect, brainstorm goals, and blog about their progress ALL inside a fitness app. Usually, fitness apps only allow you to track your progress, but this app allows you to reflect on your progress and plan for the future.
Function: The function of this web app is to provide a comprehensive and UX considered platform for users to reflect, plan, brainstorm, and blog about their fitness journey and etc.
Inputs and outputs: The inputs are the post title (text box), post content(text box), update button, create button, and delete button. The user needs to fill out and click the inputs to trigger the output. The output is the post itself, all shown in a blog format where the user can see all of their posts. The output could also be the updated post (which can be triggered by the user clicking on the text box in the post modal, changing value of the text inside, and then click the update button) and the deleted post (which wont show once the delete button is clicked and the uesr confirms deletion).
Data abstraction
- Data being stored in the database (other form of datastorage): After recieving the user's inputs, the backend will store the post title and post content in a list through the sqlAlchemy. sqlAlchemy uses .add() to add the data to the list. the data in the database represents the ID of the post, title of the post, and content of the post. The function is them given the parameter of self which is the Post database model. The name of the variable that represents the database is called "tablename".
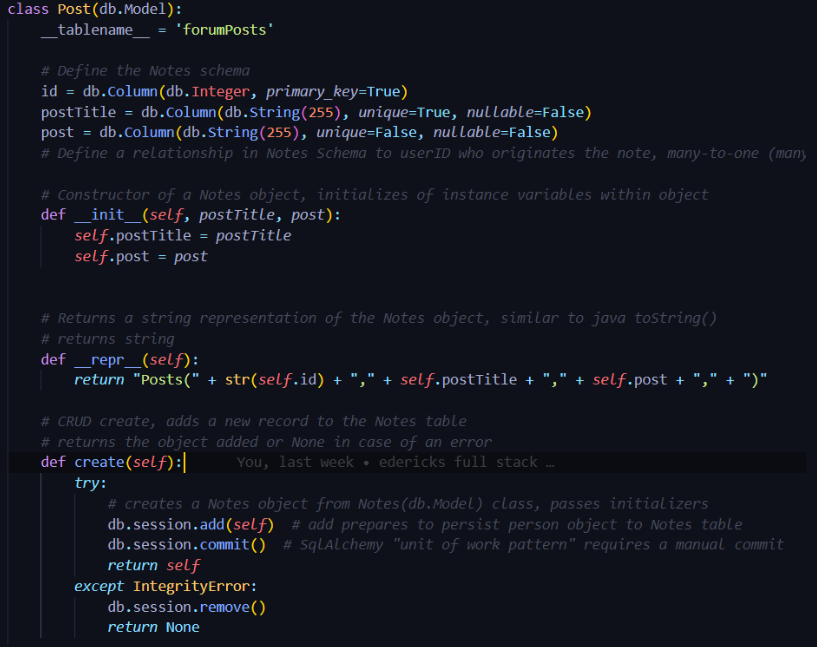
- Data from the same database being used to fullfill purpose: In the backend, there is an api endpoint called /read. This endpoint displays all the posts that the user has made, in a json format. The frontend then uses a fetch request to get the data from the backend endpoint and display it on the frontend. This is essential for the purpose of the program since there is no point of a blog if you can't see your posts. This means that the whole point of reflecting on your progress inside a fitness app is nulled.
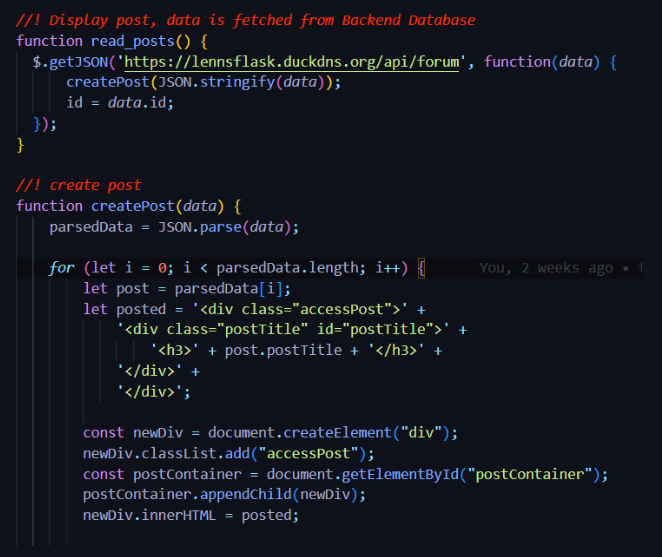
Managing complexity:
- List being used to manage complexity:
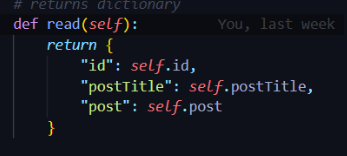
- Why the list is used: The list that is being used to manage complexity is in a function called read(). This function displays all the post data onto the frontend. To make it easier for the frontend to access post information, all of the post information is stored inside a two-dimension list. This makes it easier since the frontend can just use a for loop to access all the post information and dynamically display the post on the frontend. A different way to do this would be to use SQL Direct. This would make it a lot easier to create a function that displays all the post information. I would first have to create a connection to the database, then create a cursor object, execute a SELECT statement to fetch data, define a variable to store all the fetched data, and then create a for loop that appends all the data to the variable. This would be a lot more complex than using a JSON list.
Procedural abstraction
Student developed procedure:
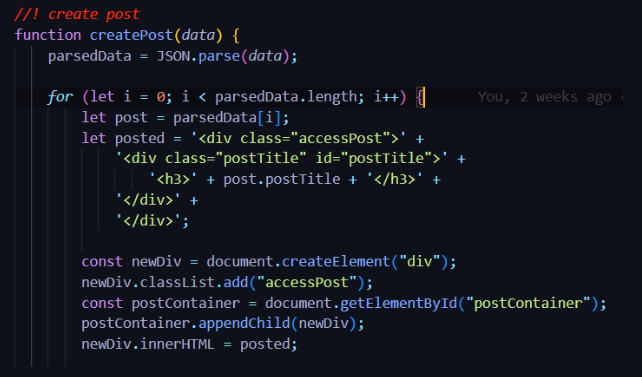
Where the procedure is called:
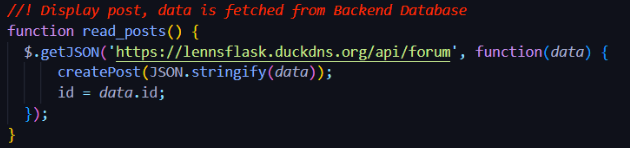
Purpose of the procedure: The purpose of the procedure is to create a post when a button is clicked. What this procedure does is it takes in data as the parameter and then assigns the data to the variable parsedData. This uses the JSON.parse() function to parse the data (which is an array) into a JSON object. Then loops through the JSON after setting i = 0 where i represents the current object in the loop. Then a variable is defined that represents the current object in the loop. Then the variable is used to access the title and content of the post, as seen in the HTML string.
Contribution to functionality: This procedure is essential to the functionality of the program since it allows the user to create a post (make an interactable post). Without this procedure, the user would not be able to display the post on the frontend after a POST request.
Algorithm implementation
Algorithm (iteration):
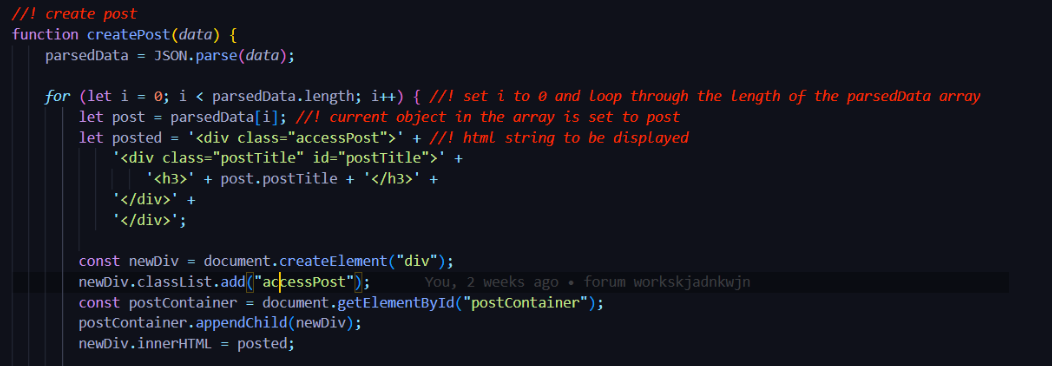
How to recreate the algorithm:
First, create a function which uses data as the parameter. This is data will then be parsed using the JSON.parse() function. Then, a for loop is created where i=0 and i is less than the length of the parsed data. Inside the for loop, a variable is defined, named post, which represents the current object in the json array called parsedData. Then, a variable is defined with the data inside the variable representing a HTML string. For the HTML string, first create a div with class of accessPost. Then create another div with the class AND id of postTitle. Now, inside postTitle, create a "h3" tag with the value of the tag being the title of the post. Remember, this is accessed by using the variable we had defined above called post. We can access the title of the post by doing post.postTitle. This can now be used to assign a new post data into a pre-formatted div. You can now create a HTML new element 'div' inside the for loop and assign it to newDiv. Then, add the class of accessPost to the new div. I had created a Wrapper for posts called postContainer. use the appendChild() function to append newDiv into postContainer. Then assign the innerHTML of newDiv to the HTML string we had created earlier.
Testing
Where the procedure is called:
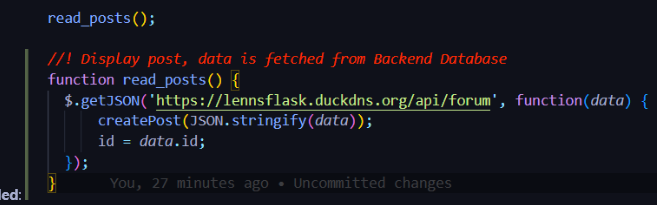
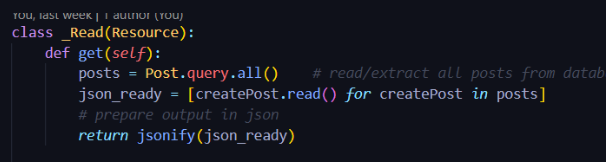
Calls to the procedure: This procedure is called everytime a post is created. This is because everytime a post is created, the procedure is called to create a new post. Basically, when a GET request is made, the procedure is called to create a new post. This is however only true when the GET request is successful. If the GET request is successful, then the procedure is called. If the GET request is not successful, then the procedure is not called and the user is not able to create a post. The condition being tested with each call to the procedure is whether or not the GET request is successful and returns a post id, post title, and post content. The result of each call is whether a new post is created or not.